When you’re enjoying the great Australian outdoors, insect bites and stings can quickly turn your adventure sour.
You’ll want to know how to handle these pesky encounters effectively. From mosquitoes to bees, each bite or sting requires a specific approach for relief and prevention of complications.
Understanding the immediate steps to take, as well as long-term care and prevention strategies, can make all the difference to your comfort and safety.
Key Takeaways
- Clean the affected sting or bite area with soap and water to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling and numb pain for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
- Use over-the-counter antihistamines or hydrocortisone cream to relieve itching and inflammation.
- Remove the sting immediately if present, using a straight-edged object to avoid squeezing the venom sac.
- Monitor for signs of severe allergic reactions from insect bites and stings and seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or persist.
Identifying Common Insect Bites
Accurate identification of insect bites and stings may require careful observation of specific characteristics, including size, shape, colour, and associated symptoms.
When identifying mosquito bites, you’ll typically notice small, round, and raised red bumps. These often appear in clusters or lines and can be intensely itchy. Mosquito bites usually develop within minutes of the bite and may persist for several days.
Recognising spider bites can be more challenging due to their variability. However, you might observe two small puncture marks at the bite site, accompanied by redness and swelling. Some spider bites, particularly those from more venomous species, may cause more severe symptoms such as pain, muscle cramps, or even necrosis of the surrounding tissue.
Bee and wasp stings often present as a single, raised welt with a visible stinger in the centre. These can be painful and may cause significant swelling.
Ant bites typically appear as small, red, raised bumps, often in a linear pattern. Flea bites are usually found in clusters on the lower legs and ankles, presenting as small, red, itchy spots.
Cleaning the Affected Area
Begin by gently washing the insect bites and stings site with mild soap and lukewarm water, taking care not to irritate the skin further. Pat the area dry with a clean, soft towel.
Next, apply an appropriate disinfecting solution to the bite or sting site. Effective options include:
- Hydrogen peroxide (3% solution)
- Chlorhexidine gluconate (0.05% to 0.5% solution)
- Povidone-iodine (10% solution)
These antiseptics will help eliminate potential pathogens introduced during the insect encounter. Apply the chosen solution using a sterile gauze pad or cotton swab, ensuring complete coverage of the affected area.
After disinfection, allow the site to air dry completely. Avoid covering the area immediately, as this may trap moisture and promote bacterial growth. Once dry, you may apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment if recommended by a healthcare professional.
Reducing Pain and Swelling

Begin by applying a cold compress to the insect bites and stings site. This can be an ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth or a bag of frozen vegetables. Apply it for 10-15 minutes at a time, several times a day. The cold constricts blood vessels, reducing inflammation and numbing the area to alleviate pain.
Topical ointments can also be effective in managing symptoms. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream (1%) can help reduce itching and inflammation. For pain relief, consider applying a lidocaine or benzocaine-based cream. Calamine lotion may soothe itching and promote healing.
If you’re experiencing severe discomfort, oral antihistamines like diphenhydramine or cetirizine can help reduce itching and swelling.
Treating Allergic Reactions
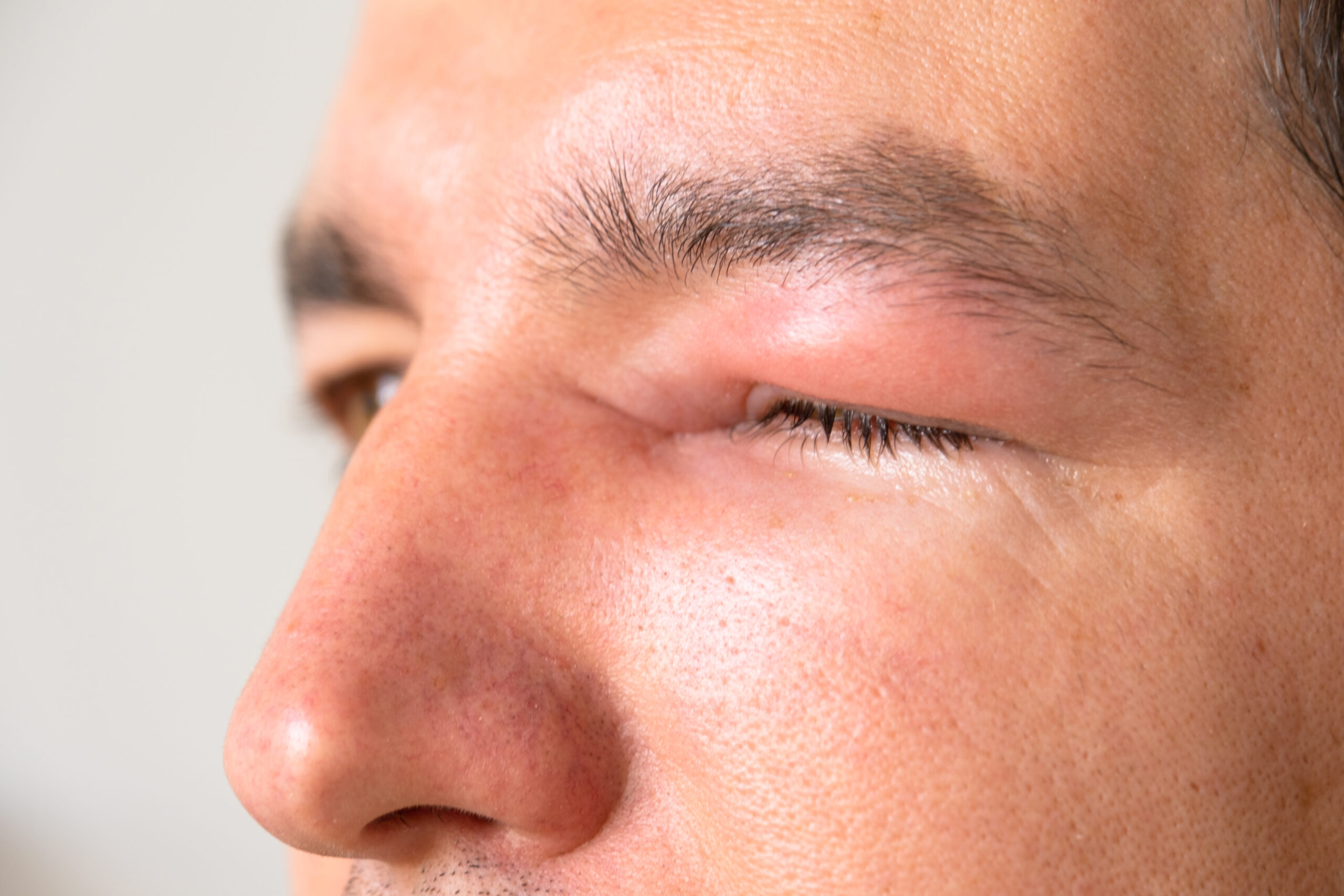
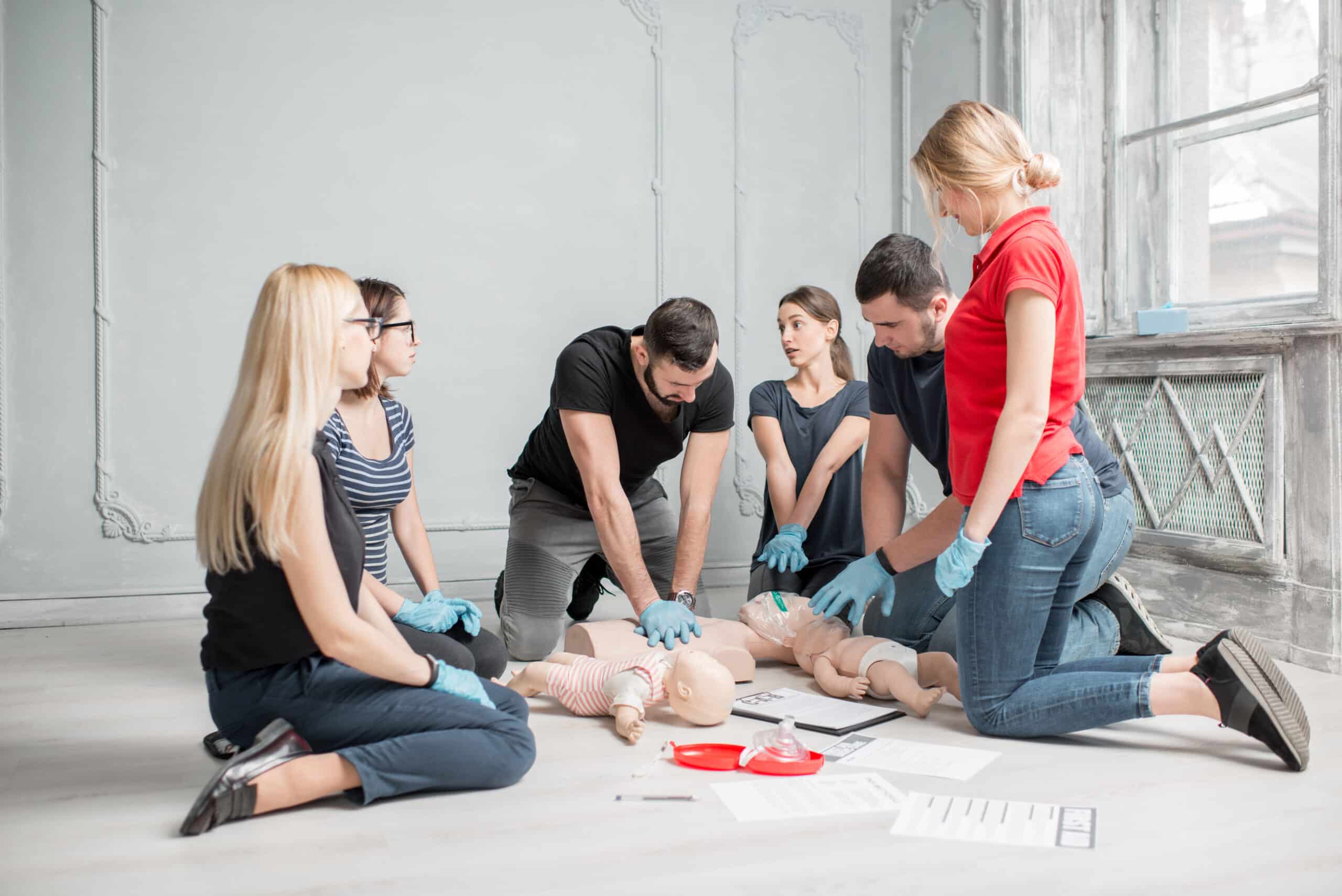
Immediate recognition of anaphylaxis symptoms is essential for initiating prompt, life-saving interventions in cases of severe allergic reactions to insect bites or stings. Anaphylaxis triggers from insect venom can lead to rapid, systemic reactions that require immediate medical attention. To effectively identify anaphylaxis, you should familiarise yourself with key recognition techniques and symptom patterns.
Watch for these vital signs of anaphylaxis:
- Respiratory distress: Wheezing, shortness of breath, or difficulty swallowing
- Cardiovascular changes: Rapid pulse, dizziness, or sudden drop in blood pressure
- Cutaneous manifestations: Widespread hives, flushing, or swelling of lips and tongue
Don’t wait for all symptoms to appear before taking action. Epinephrine administration is the primary treatment for anaphylaxis and should be given immediately upon recognition. Delayed treatment can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
Epinephrine auto-injectors are vital, life-saving devices designed to rapidly deliver a precise dose of epinephrine in cases of severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis caused by insect bites or stings. If you’re at risk for severe allergic reactions, it’s important to carry an auto-injector at all times and know how to use it properly.
Auto-injector training is essential for effective administration. To use the device, remove the safety cap, place the tip against the outer thigh, and firmly press until you hear a click. Hold for 10 seconds to guarantee complete epinephrine dosage delivery. The standard adult dose is 0.3 mg, while children typically receive 0.15 mg.
After using the auto-injector, seek immediate medical attention. The effects of epinephrine are temporary, and symptoms may return. Be prepared to administer a second dose if necessary, as advised by medical professionals.
When to Seek Medical Help

While most insect bites and stings can be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention due to the potential for severe allergic reactions or complications. It’s vital to recognise these warning signs and seek professional help promptly. A symptoms checklist can help you determine when to consult a healthcare provider.
You should seek medical help if you experience:
- Anaphylaxis symptoms: difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat or tongue, dizziness, or rapid pulse
- Signs of infection: increasing redness, warmth, swelling, or pus around the bite site
- Systemic reactions: fever, body aches, or widespread rash
If you’re unsure about the severity of your symptoms, it’s best to err on the side of caution and consult a medical professional. They can assess your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include antihistamines, corticosteroids, or epinephrine for severe allergic reactions.
Preventing Future Insect Bites
When venturing into insect-prone areas, you should prioritise covering exposed skin with long-sleeved shirts, long pants, socks, and closed-toe shoes to prevent insect bites and stings. Opt for light-coloured, tightly woven fabrics, as they’re less attractive to insects and more difficult for them to penetrate.
Insect repellent types vary in their active ingredients and efficacy:
- DEET-based repellents: Highly effective against a wide range of insects, with concentrations of 20-30% providing long-lasting protection.
- Picaridin: A synthetic compound that offers comparable protection to DEET, with less odour and skin irritation.
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus: A plant-based alternative that provides moderate protection against mosquitoes and ticks.
Apply repellents to exposed skin and clothing, following the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
For enhanced protection in high-risk areas, consider using permethrin-treated clothing or gear. This synthetic insecticide bonds to fabric fibres, creating a protective barrier against insects.
Protective gear options may include head nets, gloves, and bug jackets for thorough coverage in heavily infested environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do insect bites and stings symptoms typically last?
Most minor insect bites and stings resolve within 2-7 days. Mosquito bites usually fade within 3-4 days, while bee stings may cause swelling for up to a week. If symptoms persist beyond this timeframe or worsen, consult a healthcare provider as this may indicate an infection or allergic reaction.
Are natural remedies like tea tree oil or baking soda effective for treating insect bites and stings?
While some natural remedies may provide mild relief, they’re generally less effective than proven medical treatments. Tea tree oil can help with minor antiseptic properties, and baking soda paste may temporarily reduce itching. However, for reliable symptom management, stick to evidence-based treatments like antihistamines, hydrocortisone cream, and cold compresses.
Should children receive different treatment for insect bites and stings?
Children require the same basic care as adults but with adjusted dosages for medications. Use child-appropriate antihistamine doses, ensure epinephrine auto-injectors are the correct pediatric strength (0.15mg), and monitor children more closely as they may scratch bites leading to secondary infections. Always consult a pediatrician if you’re unsure about treatment or if symptoms seem severe.